18, March 2024
What is an ideal classroom session? Does it solely entail students following teachers’ instruction? Teacher-student interaction enhanced by varied in-class activities is a useful way teachers can facilitate engaging sessions.
On the other hand, teachers may have a hard time keeping track of individual student’s progress due to varying levels of cognition. That is where Bloom’s taxonomy proves to be an appropriate tool for evaluating students and ensuring effective teaching and learning.
What is Bloom’s Taxonomy?
Bloom’s Taxonomy is an educational framework that categorizes learning into different levels of cognition and learning objectives. Furthermore, the taxonomy has been designed as a pyramid or ladder with each step indicating higher levels of learning.
The lower levels of the taxonomy include remembering and understanding which are the building blocks for higher-order cognitive skills. Therefore, as the learners progress up the pyramid, they gain a more concrete understanding of concepts.
Benjamin Bloom published the framework in collaboration with Max Englebert, Edward Furst, Walter Hill and David Krathwol in 1956. Hence, the original six levels of the taxonomy were Knowledge, Comprehension, Application, Analysis, Synthesis and Evaluation.
However, a group of curriculum researchers, theorists and cognitive psychologists revised the framework in 2001. The revision was a vital move, helping to shift from the static objectives to establishing a dynamic and active learning process.
| The Old Version (1956) | The New Version (2001) |
|---|---|
| Evaluation | Creating |
| Synthesis | Evaluating |
| Analysis | Analysing |
| Application | Applying |
| Comprehension | Understanding |
| Knowledge | Remembering |
Three Domains Of Bloom’s Taxonomy
Bloom’s taxonomy highlights and works to improve three core learning domains that rely on particular educational outcomes.
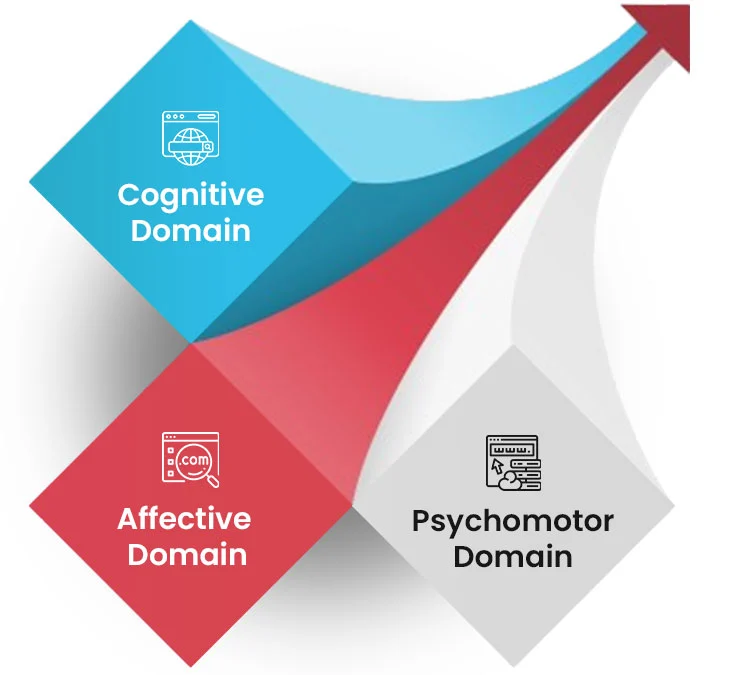
Cognitive Domain
The cognitive domain focuses on developing intellectual abilities and includes knowledge acquisition skills. Also, it focuses on developing problem-solving, decision-making and critical thinking abilities.
Affective Domain
Developing proper attitudes, values and emotional abilities is central to the affective domain. Furthermore, it focuses on helping learners develop perspectives on diverse subjects and foster motivation, social abilities and empathetic feelings.
Psychomotor Domain
Physical coordination such as hand-eye coordination is instrumental for carrying out many activities. Therefore, the psychomotor domain is one of the main components that the taxonomy focuses on.
What Is Bloom's Taxonomy? What Are Its Applications & Importance?
Primary Uses of Bloom’s Taxonomy
The revised version of Bloom’s taxonomy (2001) is one of the significant tools that teachers can use for various educational purposes such as:
- Create classroom instructional methodologies and lesson plans
- Develop teaching and learning strategies
- Design appropriate curricula
- Evaluate courses
- Create different kinds of assessments
- Figure out assessment objectives
- Provide suitable assignments and projects
- Keep track of the learning outcomes
- Monitor ongoing progress
Strategies For Effective Teaching By Using Bloom’s Taxonomy
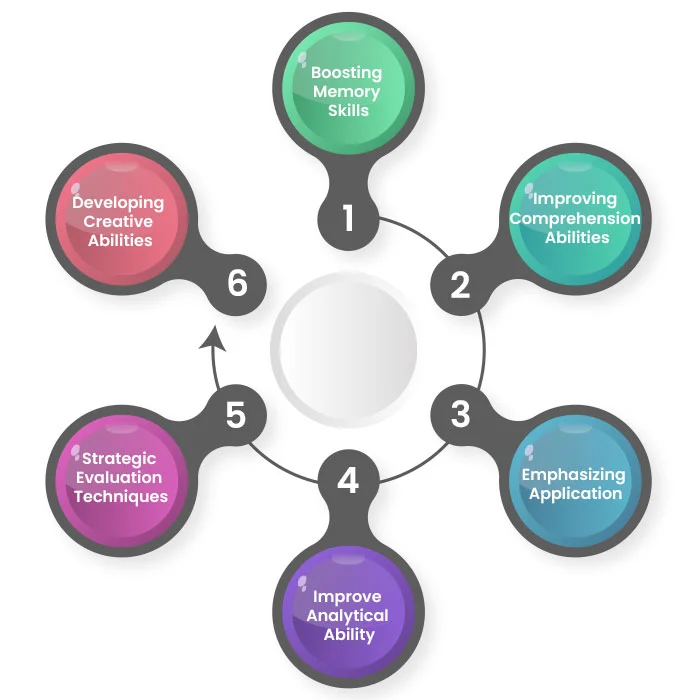
1. Boosting Memory Skills
Rote memorization is one of the commonly used techniques that most students employ to study and remember lessons and notes. This might be useful for recalling formulas or other such pieces of information but it is not effective for knowledge application.
Besides, the remembering level is the lowest level in the framework that teachers can utilize to enable students to recall key information. Hence, they can use multiple methods to boost their memory skills like the following:
- Encouraging students to create flashcards
- Conducting self-quizzes
- Using Mnemonic devices
- Using fill-in-the-blanks, impromptu quizzes, and MCQs (Multiple Choice Questions)
These activities will help to assess students’ ability to recall information such as important dates, events and formulas. Also, they must use action verbs: cite, define, describe, identify, label, list, match, name, outline, quote, recall, report, reproduce, retrieve, show, state, tabulate, and tell.
2. Improving Comprehension Abilities
Did the students understand the lesson or topics discussed in the class? Student response and engagement are two crucial indicators of the success of teaching processes. They must be able to demonstrate their understanding of multiple topics in a particular context.
Besides, knowledge acquisition or learning facts is incomplete without comprehension; that is why teachers can employ varied tactics. For example, teachers can employ short question-and-answer sessions and brief explanations.
Also, they can ask students to provide a brief summary of whatever they have learned in a specific class. Furthermore, the latter can write essays or give a short explanation of the subject and topic of the class.
Peer discussion is a productive activity that teachers can conduct in the class, allowing students to clarify key points of core topics. Action verbs: extend, extrapolate, generalize, give examples of, illustrate, infer, interpolate, interpret, match, outline, paraphrase, predict, etc.
3. Emphasizing Application
Studying for the sake of memorizing facts and passing the test is not productive in the long run because it does not add value to the learning process. For instance, learning all about litmus tests but being unable to conduct them is a case of unfulfilled application.
Hence, teachers can use several mechanisms to ensure that students can apply the knowledge they acquire in real-life scenarios. Some of the best ways to emphasize application are as follows:
- Choose and implement an effective pedagogy like project-based learning, enabling students to engage in innovative projects.
- These projects will introduce students to real-world problems, encouraging them to find solutions and apply relevant knowledge.
- Conduct lab experiments that require students to apply the knowledge at they gained from recent classes.
- Create models or presentations of machines that can help to attain sustainable development goals.
- Appropriate action verbs for application level: illustrate, implement, infer, interpret, manipulate, modify, operate, organize, outline, predict, solve, transfer, translate, etc.
What Is Pedagogy? Importance Of Pedagogy In Teaching And Learning Process
4. Improve Analytical Ability
What is the correct way to complete the assignment? How to create and stick to a schedule? How to manage time efficiently? These are some of the questions that teachers must address and solve accordingly.
Therefore, teachers must help students analyze their learning habits and use optimum methods to make better decisions. They can teach students to create mind maps, assisting the latter in making connections between different elements.
Also, picking the odd one out or drawing comparisons between two or more theories is a unique way to assess a student’s analytical ability. In addition, conducting debates or discussions on varied topics makes for engaging classroom activities.
Consequently, debates and discussions allow students to not only put forward their perspectives but also learn others’ points of view. Action verbs to test the analytical ability are discriminate, distinguish, divide, explain, identify, integrate, inventory, order, organize, relate, separate, etc.
5. Strategic Evaluation Techniques
Did I make any progress from the start of the year to the present? What have been the biggest obstacles? Was I able to accomplish the learning objectives?
These are critical questions that students must address and strive to find answers to which help to clarify their shortcomings. In fact, it relates to a vital level in Bloom’s taxonomy that indicates a high cognitive ability.
In fact, students’ ability to make wise judgements regarding all aspects of their lives is critical to their overall well-being. Hence, teachers can make use of suitable tactics to bolster the evaluation capabilities of students. Some beneficial methods are as follows:
- Peer Review - Teachers can provide an assignment or homework and upon completion, they can ask students to check each others’ work. It helps to improve their work and get a different insight which could be helpful to enhance their learning.
- Describing the advantages and disadvantages of a concept
- Maintaining a journal or diary to track thoughts and learning progress
- Review or critique a movie, product, etc
- Writing a descriptive essay and pointing out the positive or negative aspects depending on research.
6. Developing Creative Abilities
The ultimate objective of education is enabling students to create something from the knowledge that they have acquired. Moreover, they will analyze and combine different elements and create something original.
Nonetheless, they require timely guidance and instruction to know the way to arrive at an accurate conclusion. Besides, producing original work and solutions to alarming issues takes analytic thinking and self-evaluation. So, when students reach a certain level as per the framework, teachers can implement the following:
- A pedagogy with activities that urge students to make decisions based on knowledge and analytical thinking.
- Conducting brainstorming sessions
- Providing research projects and assignments
- Urging students to incorporate innovative ideas and perspectives to prepare an action plan or presentation
- Students can draft or design plans for disaster management.
Bloom’s Taxonomy And Technology Integration In The Classroom
Tips for Successful Bloom’s Taxonomy Implementation
- Teachers must use clear and concise learning objectives or outcomes, helping students and teachers to understand the goals. Also, it helps them understand the abilities that they would demonstrate by the course’s end.
- An ideal example of a learning objective is students will be able to describe the contributing factors of the industrial revolution.
- Plan appropriate instructional strategy according to the various levels/hierarchy of the taxonomy by progressing from fundamental to complex.
- Determine the learning gaps and needs of the students to ensure the necessary alignment of the taxonomy and teaching strategies.
- Check student’s prior knowledge and understanding by asking open-ended questions.
- Design and use flexible content, allowing students of varying comprehension levels to engage and respond. Additionally, they can use LMS to develop different kinds of learning content containing multiple questions, such as MCQs, microlessons, etc.
Conclusion
Bloom’s taxonomy is a significant pedagogical framework that teachers can use to develop instructional approaches. Also, it serves as a reference to improve the learning habits of students and foster cognitive abilities. Students succeed in accomplishing set goals and learn essential skills.
Still wondering about how to develop better student learning outcomes? Learn the best uses of Bloom’s Taxonomy.
Mobile: 08448010216
Email:info@mastersofterp.com













