19, Feb 2024
In today's dynamic global landscape, where the exchange of information, ideas, cultures, and resources transcends borders, we find ourselves intricately connected. Simultaneously, we also face common global challenges—climate change, poverty, inequality, migration, conflict, and human rights violations.
These challenges require a collective response, and international cooperation, coupled with critical thinking and empathy. How can we prepare students to face these challenges and contribute to a more peaceful, just, and sustainable world?
This is where the concept of Global Citizenship Education (GCED) steps in. GCED is a form of learning that aims to equip learners with the knowledge, skills, values and attitudes to become responsible and active global citizens.
In this blog post, we will explore what Global Citizenship Education is, why Global Citizenship Education is important for students, how School ERP can facilitate its implementation, and what challenges and opportunities lie ahead.
Exploring Global Issues: A Primer On Global Citizenship Education
Understanding Global Citizenship Education (GCED)
In the ever-evolving and interconnected global society, Global Citizenship Education emerges as a form of civic learning, transcending the conventional boundaries of education. It is an approach that can be integrated across subjects and disciplines, as well as in formal, non-formal and informal settings.
GCED covers three domains of learning: cognitive, socio-emotional and behavioural.
Cognitive Domain
The cognitive domain of GCED delves into the intellectual aspects, emphasising the acquisition of knowledge and understanding of global issues.
Learners are challenged to explore the causes, consequences, and potential solutions to these complex global challenges. This domain acts as the intellectual cornerstone, fostering a nuanced understanding of the intricacies that characterise our global community.
Socio-emotional Domain
In the socio-emotional domain, GCED seeks to cultivate a range of values and attitudes essential for responsible global citizenship. This includes fostering respect for human rights and diversity, instilling empathy for others, promoting solidarity with marginalised groups, and instigating a profound sense of global responsibility.
Additionally, it endeavours to nurture emotional intelligence, enabling learners to manage their emotions, navigate stress, resolve conflicts, and collaborate effectively with others.
Behavioural Domain
The behavioural domain requires students to translate their understanding and values into tangible actions. This involves addressing global issues at both local and global levels, developing effective communication skills across diverse audiences, participating in democratic processes, advocating for change, and leading by example.
The behavioural domain embodies the transformative power of education, emphasising the potential to drive positive change on a global scale.
These three domains are interrelated, reinforcing one another. Aligned with UNESCO's four pillars of education—learning to know, learning to do, learning to be, and learning to live together—GCED provides a holistic framework for comprehensive learning.
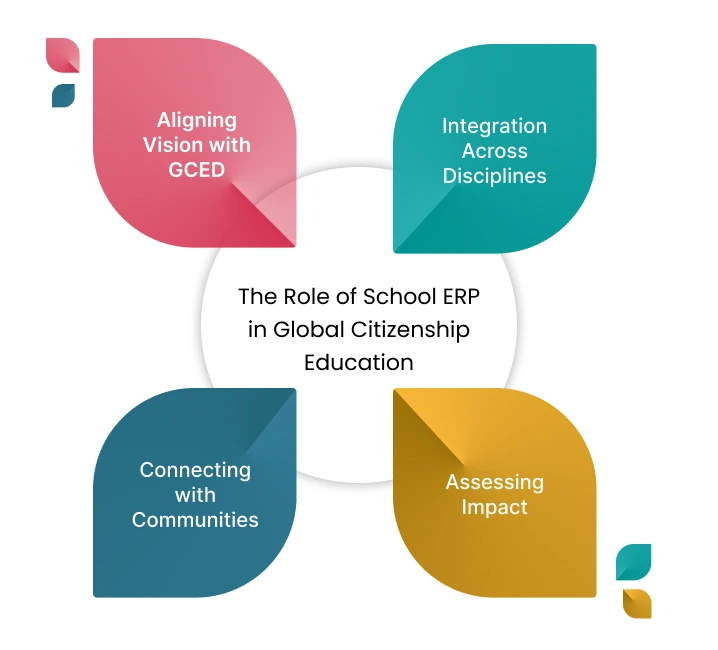
The Role of School ERP in Global Citizenship Education
School Enterprise Resource Planning (School ERP) emerges as a versatile and integral tool designed to assist schools in efficiently managing their resources. From admissions and attendance to assessments, timetables, libraries, and beyond, School ERP encompasses a broad spectrum of functions.
But how can this technological tool facilitate the complex and multifaceted implementation of GCED within educational institutions?
Aligning Vision with GCED
In the pursuit of aligning institutional vision, mission, and goals with the principles of GCED, School ERP takes centre stage. By seamlessly incorporating GCED values into school policies, codes of conduct, curricula, and extracurricular activities, School ERP becomes a catalyst for fostering a culture steeped in global citizenship.
Integration Across Disciplines
School ERP emerges as an invaluable ally in the seamless integration of GCED across subjects and disciplines. By providing educators with robust tools for curriculum design, lesson planning, assessment, and feedback, it empowers teachers to seamlessly incorporate GCED principles into diverse areas of study.
This capability extends to designing interdisciplinary projects that encourage active participation and engagement from students.
Connecting with Communities
A key strength of School ERP lies in its capacity to facilitate the establishment of connections with local and global communities. By offering robust platforms for communication, collaboration, and exchange, this tool empowers schools to forge meaningful partnerships with other educational institutions, NGOs, UN agencies, and more.
These connections provide invaluable avenues for sharing best practices, resources, and research related to GCED.
Assessing Impact
School ERP enables schools to gauge the impact of GCED through comprehensive data collection, analysis, and visualization. In a data-driven educational landscape, this tool allows schools to measure not only academic outcomes but also students' evolving attitudes and behaviors concerning GCED.
This iterative process facilitates continuous improvement and refinement of GCED programs and activities.
The Importance of GCED Skills for Students
GCED skills extend beyond academic achievement; they are important for personal growth and societal contribution. These skills empower students to develop the mindset and actions synonymous with global citizenship, a designation that encompasses a rich tapestry of attributes.
A global citizen is someone who possesses a multifaceted set of characteristics, including:
- Awareness of Interconnectedness : Understanding the profound interconnectedness and interdependence of the world and its people
- Respect for Diversity : Exhibiting respect for human rights and diversity, embracing the richness of different perspectives and cultures
- Empathy and Compassion : Demonstrating empathy and compassion towards others, fostering a genuine understanding of shared humanity
- Commitment to Global Justice : Advocating for and actively contributing to global justice and solidarity
- Responsibility and Accountability : Taking responsibility and accountability for individual actions and their collective impact on the world
- Proactivity and Creativity : Exhibiting proactivity and creativity in finding innovative solutions to complex global problems
A global citizen possesses the ability to navigate the intricacies of global issues, showcasing critical thinking and creativity in understanding their causes, effects, and potential solutions.
The Importance Of Global Citizenship Education In A Connected World
Effective communication skills allow them to engage with diverse audiences and stakeholders, fostering collaboration and tangible actions to advocate for change at both local and global levels.
These GCED skills align seamlessly with the evolving demands of the 21st-century workforce. According to a report by the World Economic Forum, the top 10 skills that employers will seek in 2025 include:
- Analytical Thinking
- Active Learning
- Complex Problem-Solving
- Critical Thinking
- Creativity
- Leadership
- Technology Use
- Resilience
- Reasoning
- Problem-Solving
These skills closely mirror the cognitive, socio-emotional, and behavioural domains emphasised in GCED.
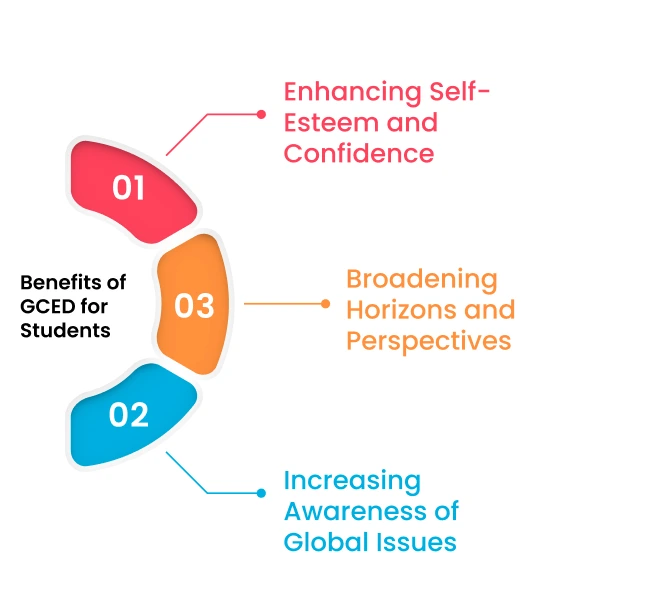
Benefits of GCED for Students
The benefits of Global Citizenship Education extend beyond the academic realm, impacting students personally and professionally. These advantages encompass a nuanced range of outcomes.
Enhancing Self-Esteem and Confidence
GCED serves as a catalyst for enhancing students' self-esteem, confidence, motivation, and resilience. By encouraging self-discovery, GCED encourages students to identify their strengths, interests, values, and aspirations. Moreover, it equips them with the skills to tackle challenges, uncertainties, and failures with a resilient mindset.
Broadening Horizons and Perspectives
Global Citizenship Education acts as a powerful trigger in broadening students' horizons, perspectives, and opportunities. It exposes them to diverse cultures, histories, realities, and possibilities. By promoting access to new information, resources, networks, and opportunities, GCED empowers students to explore and embrace the richness of our globalised world.
Increasing Awareness of Global Issues
At its core, Global Citizenship Education increases students' awareness of global events and issues. By simplifying the complexity and interrelatedness of global challenges such as poverty, inequality, climate change, migration, conflict, and human rights violations, GCED empowers students to comprehend the opportunities and responsibilities they bear in contributing to a more peaceful, just, and sustainable world.
Challenges in Implementing GCED in Schools
Despite the evident importance and benefits of Global Citizenship Education, schools encounter several challenges in its effective implementation. These challenges are multifaceted and demand effective approaches for resolution.
Lack of Policy Support and Recognition
One common challenge is the lack of thorough policy support and recognition for Global Citizenship Education in National Education Frameworks. Often, GCED is not explicitly included or prioritised in educational policies, curricula, standards, or assessments. This absence of formal recognition hinders its widespread adoption and implementation in educational institutions.
Insufficient Resources and Capacity
Many educational institutions struggle with a persistent shortage of financial, human, material, and technological resources necessary for the effective implementation of GCED. From designing and delivering programs to monitoring and evaluating their impact, schools face limitations in their capacity to fully embrace and integrate GCED into their educational frameworks.
Limited Awareness and Understanding
A critical challenge arises from limited awareness and understanding of Global Citizenship Education among various stakeholders, including teachers, students, parents, and communities. Teachers may lack the requisite knowledge, skills, values, and attitudes to effectively teach GCED.
Simultaneously, students may lack the interest, motivation, or engagement required for active participation in GCED activities. Furthermore, parents and communities may lack the awareness or support needed to champion GCED within the school environment.
How Going Paperless By Using School ERP Software Helps Educational Institutions?
The Future of Global Citizenship Education
In emphasising the importance of Global Citizenship Education, it surpasses the domain of being a luxury or an optional educational approach; it emerges as a necessity and an obligation for the future of education and humanity.
Aligned with the global commitment of the Education 2030 Agenda—a commitment to ensure inclusive and equitable quality education and lifelong learning for all by 2030—Global Citizenship Education is recognized as one of the key skills essential for navigating the complexities of the 21st century.
GCED further aligns with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), a set of 17 goals and 169 objectives aimed at ending poverty, protecting the planet, and ensuring peace and prosperity for all by 2030. These goals, interconnected and interdependent, necessitate global citizenship and international cooperation for their realisation.
Final Thoughts,
In conclusion, Global Citizenship Education stands as an indispensable and transformative approach, empowering students to develop the knowledge, skills, values, and attitudes needed to become responsible and active global citizens. It goes beyond the realms of personal growth, impacting academic and professional success by fostering critical thinking, effective communication, collaboration, creativity, and problem-solving skills.
With tools like School ERP, educational institutions can seamlessly integrate Global Citizenship Education into their culture, connecting with communities and preparing students for the challenges and opportunities of the 21st century.
By fostering collaboration among educators, students, parents, and communities, we can collectively contribute to creating a more peaceful, just, and sustainable world—a world where global citizenship is not just a concept but a lived reality.
The Future Is Here: Next-Generation Solutions for Higher Education
Mobile: 08448010216
Email:info@mastersofterp.com













