08, Jan 2023
An education system that addresses the challenges and demands of the ever-evolving world is a significant part of nation-building. Therefore, taking appropriate initiatives and campaigns that reflect the ethos and mission of the country is the primary step.
That is why NEP 2020 was a landmark decision in the direction of facilitating high-quality education. Furthermore, its major goal is to develop thoughtful, well-rounded, and creative individuals who can contribute to the community.
Therefore, an Institutional Development Plan (IDP) is a vital strategy that allows institutes to implement the practices to achieve the aims of the policy.
National Education Policy 2020: All You Need To Know About NEP 2020 For Schools
What is an institutional development plan?
An institutional development plan refers to a plan of action or a set of directives that pivots the institutes towards academic and professional achievement. Furthermore, the University Grants Commission (UGC) has provided guidelines for institutes to prepare elaborate IDPs.
These guidelines recognise the diversity of sociocultural traditions, languages, and various aspirations and expectations. Therefore, the emphasis is to avoid a monolithic or single-dimensional approach to quality and standards in higher education.
Moreover, it stresses that different components of IDP must empower institutes to accomplish academic and research excellence. It must incorporate learner-centric teaching, knowledge creation, dissemination, and application of skills and knowledge.
Institutional Development Plan Framework and Its Major Components
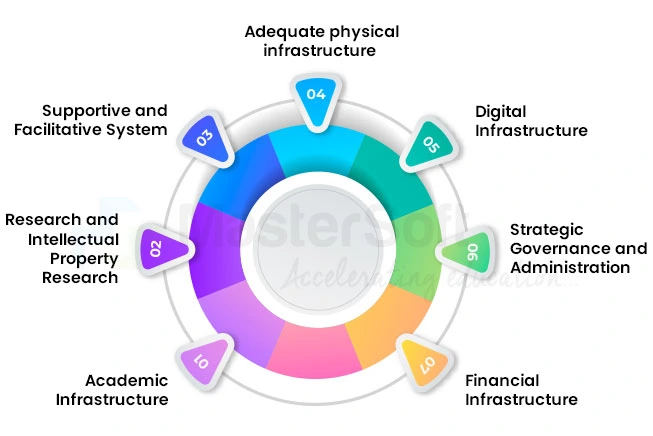
1. Academic Infrastructure
How can we ensure students’ continuous progress? How do I determine the academic pitfalls? How do you facilitate productive and insightful feedback for students? These are some of the questions that academic infrastructure must address and provide answers to.
Besides, a good and effective academic infrastructure assures a healthy and enriching learning environment that leads to better student performance. It is the institute’s responsibility to create a positive environment and ensure students' physical and mental well-being.
Institutes can create a successful academic infrastructure in the following ways:
- Conduct institutional SWOC analysis, which helps to assess the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and challenges of the institute.
- Develop unique and better practices by doing ABC analysis.
- Utilise technological solutions like the educational ERP for predictive analysis, aiding in current and future strategies.
- Conduct faculty performance analysis and regular training to create and retain competent faculty.
- Design a modern and flexible curriculum and include multidisciplinary aspects such as the integration of vocational education, training, and skilling.
- Implementing a confidence-building education model through a student-integrated development model.
- High-quality professional and application- or experiential-based education in a wide range of interdisciplinary areas.
- Inculcating employability skills like life skills, soft skills, and foundational technology skills in the learning
- Curriculum for sensitization in terms of providing educational programmes for inculcating virtues like empathy and also towards the environment, PwDs, and other special sections of society
2. Research and Intellectual Property Research
Basic research, general-purpose technologies, and ideas have an overarching significance in society's development. It influences varied sociocultural and economic factors such as information production, education, community building, socialisation, etc.
Research and intellectual property research lead to the improvement of the 4Cs (critical thinking and analysis, creativity, communication, collaboration and teamwork). Also, it helps to drive the internationalisation of education.
Consequently, it enables the improvement of the Indian education system and aligns it with global standards. Therefore, the institutes must involve all stakeholders in research, innovation, and documentation in the form of scholarly publications.
They must encourage systematic institutional research with high performance and output at a low cost. Also, they can strengthen joint research and publications by collaborating with numerous research universities and research centres.
Conduct training sessions and programmes that focus on educating the staff and researchers about IP protection and research monetization. They can collaborate with industry stakeholders through technology-sharing agreements and collaborative projects.
Consequently, it will help create pathways for commercialization and gain market insights.
NCFTE: Guide On National Curriculum Framework For Teacher Education
3. Supportive and Facilitative System
Creating an inclusive and adequate support system that creates a sense of security, ownership, and pride is a vital requirement. This includes ensuring a good working environment for all stakeholders with the help of ethical policies.
On the other hand, a transparent academic and administrative system provides the necessary conditions to develop support and facilitative infrastructure. Institutes can consider the following steps to develop emotional surplus:
- Create an atmosphere of mutual trust and respect between stakeholders.
- Develop core values of dedication, commitment, and service between the institutes and stakeholders, a key objective of the institutional development plan.
- Inculcate diversity in the composition of students, faculty, and staff in terms of gender, class, religion, region, caste, and nationality.
- Make sure all institute buildings and facilities are PwD (persons with disabilities) friendly.
- Provide socio-emotional and academic support and mentoring for all students through appropriate counselling and mentoring programmes.
- Encourage the sensitization of faculty, counsellors, and students on issues related to gender identity and its inclusion in all aspects of higher education.
- Establish anti-discrimination and anti-harassment rules and internal committees to deal with sexual harassment cases.
4. Adequate physical infrastructure
Institutes must invest generously to provide the appropriate infrastructure that supports academic and research activities. For instance, in the case of public institutes, the government must provide sufficient funds to facilitate basic and specialised infrastructure.
On the other hand, private institutes and universities can seek sponsoring organisations to accomplish the aim. However, intense competition in the higher education service business has led to borrowing money from banks and lenders with high-interest rates.
Hence, it is essential to seek alternative avenues to finance their physical infrastructure, which must have the following facilities:
- Adequate infrastructure facilities and equipment have been provided or integrated with departments for vocational education, training, and skilling.
- Availability of basic health facilities, including mental health services like psychological counselling and wellbeing centres.
- Conducting energy efficiency practices.
- Various parts of the campus are accessible to PwD students. The campuses comply with the integration of all genders and have zero tolerance for ragging, gender-based discrimination, bullying, etc.
- Following green initiatives means minimising carbon footprints, preserving natural resources, and conserving water.
5. Digital Infrastructure
Digitalization is a modern phenomenon that has not only automated administrative tasks but also revolutionised the educational system. The integration of ICT (Information and Communication Technology) has specifically impacted the overall functionality.
For instance, tools like the educational ERP have led to improved learner experience, low operational costs, smooth communication, and improved decision-making. Additionally, ICT features elevate the teaching and learning process, making it more engaging.
Hence, it is only fitting that institutes take the necessary steps to make optimal use of digital infrastructure in the following ways:
- Developing an online learning platform with a two-way video and audio mechanism and assistive learning tools will help track learners' progress.
- Provide efficient and robust ICT infrastructure in all parts of the campus, facilitating high-speed connectivity, communication, and access.
- Availability of a digital repository of content such as learning games and simulations, sandboxes and playful learning, augmented reality and virtual reality, coursework, cases, etc.
- Ensure easy access, secure data, enhance mobility of students, faculty, and staff, facilitate credit transfers, and support Academic Bank of Credit (ABC), besides creating a centralised infrastructure to ensure the credibility of the system and policy framework.
- Create a robust digital infrastructure that includes a paperless office system using an automatic learning management system. The system must facilitate digital information processing services for all teaching, learning, examination, and evaluation activities.
- They must automate significant institutional operations with the help of e-tech tools and simplify enrollment, examination, and evaluation processes.
What Is Academic Bank Of Credits (ABC) In Higher Education Institutions?
6. Strategic Governance and Administration
Governance is the way an institution functions, and it depends upon the processes and structure for decision-making, accountability, and risk reduction. It includes relationships and processes through which institutes develop, implement, and review policies.
One of the fundamental reasons for good governance is that it provides the foundation for a sustainable, high-performing organisation. It helps to determine how the institute responds to the changing external environment.
Strategic governance and administration are also key players in the implementation of the institutional development plan. It ensures institutional success through an emphasis on accountability and improved performance. Therefore, the best way to improve governance is through the following:
- Incorporating elaborate processes and quality assurance mechanisms.
- Including all stakeholders, including alumni, in the processes that lead to appointments, nominations, and selections in the BoG, Senate, and Syndicate
- Various levels of financial autonomy exist, including striving for self-sustainability.
- Establishing effective leadership, strategic decision-making, and operational efficiency.
7. Financial Infrastructure
A robust financial infrastructure is one of the critical prerequisites of institutional operation, which may impact all the other processes. This is where technical systems prove to be instrumental in dealing with payments and financial instruments.
There must be a continuous effort from the institute's leaders to improve the financial infrastructure. They can seek government grants, alumni donations, private-sector partnerships, and fundraising campaigns to develop financial infrastructure. They must consider the following aspects:
- Budget Allocation: Institutes must determine the budget allocation in different areas of the institution, including infrastructure development, faculty and staff salaries, etc.
- Transparency: Ensure transparency and accountability in all financial transactions, helping to maintain credibility among stakeholders.
- Investment Strategy: Prepare an investment strategy that ensures returns on investment (ROI) with minimum risks.
- Financial Collaboration: Facilitate collaborations and partnerships with government agencies, private sector entities, and other institutions. Consequently, it will support the development of financial infrastructure and secure resources.
Final Thoughts,
Academic progress and institutional success must go hand in hand to contribute to the education system. However, that does not happen due to ineffective policies and methodologies that do not align with the goals. Hence, the institutional development plan plays a crucial role in establishing a transparent system for the holistic and inclusive growth of the institute.
Streamline Teaching-Learning Process with MasterSoft’s Learning Management System.
Mobile: 08448010216
Email:info@mastersofterp.com













