24 November 2023
The National Education Policy 2020 (NEP 2020) is a comprehensive framework aimed at transforming the country's education system. This detailed guide explores the key features, objectives, challenges, the implementation plan of the NEP, and NEP compliance, providing an in-depth understanding of its impact and significance in reshaping the educational landscape of India.
Key Features of NEP 2020:
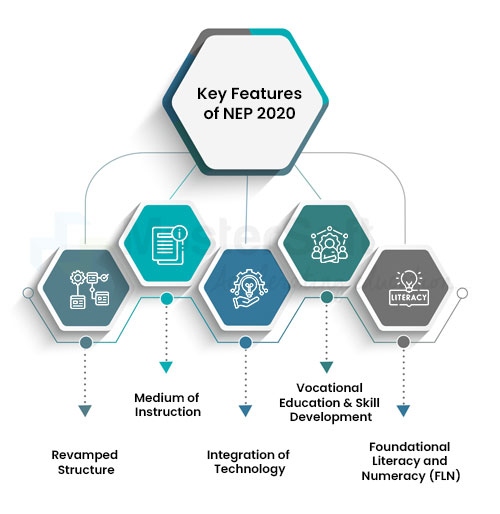
Revamped Structure:
The NEP 2020 introduces a new academic structure, moving from the traditional 10+2 format to a more modernised 5+3+3+4 structure. This alteration divides the education system into four stages: Foundational, Preparatory, Middle, and Secondary.
NEP 2020 New Academic Structure Explained - 5+3+3+4 Education System
Medium of Instruction:
The policy places a significant emphasis on using the mother tongue as the medium of instruction, fostering better understanding and communication in early education.
Integration of Technology:
Recognising the role of technology in education, NEP 2020 encourages the use of digital tools and platforms to enhance learning outcomes and accessibility.
Vocational Education and Skill Development:
The National Education Policy 2020 emphasises the importance of vocational education, aiming to equip students with practical skills for real-world applications.
Foundational Literacy and Numeracy (FLN):
The NEP 2020 policy highlights the significance of foundational literacy and numeracy, aiming to bridge knowledge gaps and ensure basic skills among students.
Let’s understand in detail the key objectives of National Education Policy 2020.
Objectives of NEP 2020:
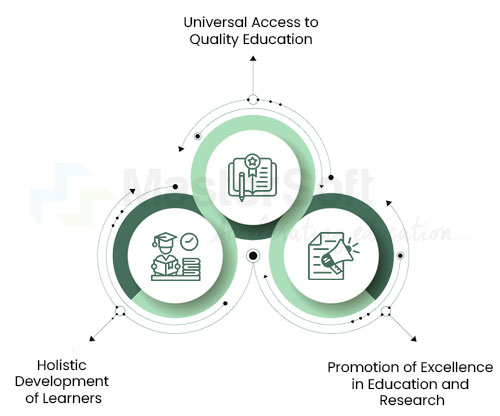
The National Education Policy 2020 outlines three primary objectives, each contributing to the overall advancement of the education system.
Universal Access to Quality Education:
- Ensure access to quality education for every child in India.
- Overcome socio-economic barriers to education.
Promotion of Excellence in Education and Research:
- Foster innovation, creativity, and entrepreneurship in the education sector.
- Encourage and support research and development in various fields.
Holistic Development of Learners:
- Facilitate the cognitive, emotional, social, and physical development of learners.
- Strive to create well-rounded individuals capable of contributing meaningfully to society.
Implementation Plan for NEP:
Short-term (2020-2022):
Focuses on immediate initiatives like revising the curriculum, teacher training, and integrating technology into the education system.
Medium-term (2023-2026):
Concentrates on the implementation of key reforms, including the establishment of a National Assessment Centre and the development of a new Curriculum Framework.
Long-term (2027-2030):
Aims at consolidating reforms, achieving key policy goals such as 100% literacy, and establishing a vibrant research culture in Indian universities.
This plan is set in motion and has already seen positive outcomes. Now, let's understand its evolution.
Evolution of NEP:
The guide traces the evolution of the National Education Policy from its inception in 1986 to the transformative changes introduced in 2020. It emphasises the shift in focus from equality and open universities to the 2020 policy's goal of aligning with Sustainable Development Goals and transforming education for the 21st century.
It has some fundamental principles, which include:
Fundamental Principles of NEP:
The National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 is founded on a set of core principles that shape the direction of education in India.
Recognition of Unique Student Capabilities:
- Acknowledge and nurture the distinct learning styles, interests, and competencies of each student.
- Sensitise teachers and parents to understand and appreciate the individuality of students, fostering confidence and growth.
Foundational Literacy and Numeracy:
- Ensure that every student, by the third grade, possesses foundational literacy and numeracy skills.
- Prioritise a child's ability to read basic texts and solve fundamental mathematical problems.
Flexibility in Career Trajectory:
- Provide students with the flexibility to choose their career paths based on their interests.
- Recognise and support diverse inclinations, be they in mathematics, sports, the arts, or other fields.
Elimination of Hard Separations:
- Discourage rigid divisions between curricular and extracurricular activities, as well as between science and the arts.
- Emphasise equal attention to all subjects and activities, fostering a well-rounded education.
Multidisciplinarity and Holistic Education:
- Encourage the integration of diverse fields of knowledge to ensure a comprehensive learning experience.
- Strive for unity and integrity in all forms of knowledge, moving beyond traditional, textbook-centric education.
Emphasis on Conceptual Understanding:
- Prioritise in-depth comprehension of concepts over rote memorization.
- Counter the trend of memorising for exams without fostering a genuine understanding of the subject matter.
Promotion of Creativity and Critical Thinking:
- Cultivate logical thinking and innovation among students.
- Foster independent thinking by recognising and promoting the unique capabilities of students, teachers, and parents.
Ethics and Human Values:
- Instil values such as empathy, respect, cleanliness, courtesy, and democratic spirit in education.
- Emphasise the importance of ethical behaviour, social responsibility, and adherence to constitutional values.
Promotion of Multilingualism:
- Acknowledge and celebrate the linguistic diversity of India.
- Encourage educational institutions to promote multilingualism in teaching and learning.
Life Skills Development:
- Integrate the teaching of essential life skills such as communication, resilience, problem-solving, and perseverance.
- Equip students with abilities that go beyond academic knowledge, preparing them for real-world challenges.
Focus on Formative Assessment:
- Implement regular formative assessments to identify and address students' strengths and weaknesses.
- Utilise assessments to assist teachers in recognising gaps in knowledge and providing targeted support.
Extensive Use of Technology:
- Harness technology for improved teaching and learning experiences.
- Leverage technology to overcome barriers, enhance management efficiency, and facilitate better education delivery.
Respect for Diversity and Local Context:
- Respect and incorporate cultural nuances and examples from local contexts into educational materials.
- Ensure that textbooks reflect the rich cultural heritage of India, promoting better comprehension and understanding.
Full Equity and Inclusion:
- Prioritise equity and inclusion to bridge gaps in access, participation, and learning outcomes.
- Ensure that every child, regardless of socio-economic status, has access to quality education.
Synergy in Curriculum Across Levels:
- Ensure a cohesive curriculum design across all levels of education.
- Systematically introduce concepts, providing precise guidance to students from early childhood education to higher education.
Teacher-Centric Approach:
- Recognise teachers and faculty as central to the learning process.
- Emphasise their recruitment, professional development, and overall well-being to enhance the education system.
Commitment to Outstanding Research:
- Advocate for extensive research to maintain high educational standards.
- Support initiatives that contribute to the advancement of knowledge and quality education.
Continuous Review and Feedback:
- Emphasise the importance of continuous and consistent reviews to assess progress.
- Use feedback mechanisms to identify successful practices and areas for improvement.
In essence, the principles of NEP 2020 aim to create an inclusive and high-quality education system, providing students with the tools for a better standard of living.
Let's understand in detail about NEP compliance.
NEP Compliance: Navigating the Digital Transition in Indian Education
The National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 has ushered in a transformative era for Indian education, with a particular emphasis on digitization and technology integration.
Ensuring NEP compliance involves navigating the complexities of this digital transition, and this section delves deeper into the strategies and considerations that educational institutions can adopt to align with the policy guidelines.
NCF 2020 (National Curriculum Framework - 2020) - A Complete Guide
1. Seamless Integration of Digital Learning Platforms:
NEP 2020 underscores the importance of digital learning platforms as essential tools for providing students with access to diverse educational resources. Schools need to seamlessly integrate these platforms, offering a wide range of multimedia resources such as videos, animations, and interactive simulations.
The focus should be on creating an immersive learning experience that goes beyond traditional classroom boundaries.
2. Learning Management Systems (LMS) for Enhanced Learning:
An effective Learning Management System is pivotal in the NEP-compliant educational ecosystem. It allows educators to create, manage, and deliver online learning content. An ideal LMS should provide students access to online assignments, quizzes, and tests while also enabling educators to track student progress and analyse performance data.
This fosters a student-centric approach and aligns with NEP 2020's goal of personalised and flexible learning pathways.
3. Digital Libraries for Access to Knowledge:
The creation of digital libraries is integral to NEP compliance. These libraries, housing ebooks, journals, and articles, should be accessible to students, teachers, and staff. This not only facilitates easy access to a wealth of information but also aligns with NEP's emphasis on promoting research and innovation in educational institutions.
4. Online Collaboration Tools for Enhanced Engagement:
The NEP envisions a collaborative learning environment, and online collaboration tools play a crucial role in achieving this objective. Platforms like Google Classroom, Microsoft Teams, and Zoom enable students and teachers to work together on projects, assignments, and presentations in real-time.
This collaborative approach nurtures essential skills like teamwork and communication, aligning with NEP's broader goals of holistic development.
5. Video Conferencing for Real-Time Communication:
Real-time communication is a cornerstone of NEP implementation. Video conferencing tools like Zoom and Microsoft Teams facilitate seamless interaction between students and teachers, overcoming geographical barriers and promoting effective teacher-student engagement.
This synchronous mode of communication enhances the learning experience and supports NEP's vision of inclusive education.
6. Cloud-Based Storage for Accessibility and Security:
The NEP recognises the need for a robust digital infrastructure, and cloud-based storage is a key component of this infrastructure. Schools should adopt secure cloud-based storage solutions that allow for the storage and sharing of files.
This ensures accessibility to important documents and materials from anywhere, at any time, fostering a flexible and inclusive learning environment.
7. Interactive Whiteboards and Displays for Engaging Learning:
Interactive whiteboards and displays contribute to making learning more interactive and engaging. The integration of such tools aligns with NEP's focus on fostering creativity and critical thinking.
These technologies provide educators with innovative methods to deliver lessons, enhancing the overall learning experience for students.
8. Educational Applications for Diverse Learning Needs:
NEP compliance necessitates catering to diverse learning needs. Schools should invest in a range of educational applications suitable for students of different ages and abilities.
These applications should not only provide access to digital learning resources but also facilitate real-time data and analytics on student performance, supporting the policy's emphasis on continuous assessment and improvement.
9. Cybersecurity Measures for Data Protection:
With the increasing reliance on technology, cybersecurity becomes paramount. Schools should implement robust measures, including firewalls, antivirus software, and regular security updates, to safeguard against cyber-attacks and data breaches.
NEP compliance requires a secure digital environment, ensuring the privacy and integrity of student information.
National Education Policy 2020: All You Need To Know About NEP 2020 For Schools
10. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) for Efficient Administration:
An ERP system streamlines administrative tasks, such as managing student information, staff details, financial records, and inventory information.
This centralised system ensures efficient and organised administration, aligning with NEP's objective of promoting effective governance and management in educational institutions.
Summing Up,
NEP compliance in the digital age demands a holistic and strategic approach to technology integration. Educational institutions need to leverage the full potential of digital tools and platforms, fostering an environment that aligns with the policy's vision of inclusive, flexible, and personalised education.
By embracing these technological advancements, schools can not only meet the guidelines set by NEP 2020 but also pave the way for a future-ready education system in India.
Connect With MasterSoft - Your One-Stop ICT Solutions Aligned With NEP 2020
Mobile: 08448010216
Email:info@mastersofterp.com

















